Asphalt Surface Course
Asphalt Surface Course - Special cases as directed by bureau of materials. The stiffness increases rut resistance, but makes it more likely to crack. In addition, it serves as a waterproofing layer to. Most conventional existing analysis models do not directly account for the continuous grading of properties in flexible pavement layers. Demolition and removal is completed using heavy machinery, including small bobcats and forklifts and when necessary, front loaders and large dump trucks. Asphalt is an industrial material made by mixing aggregates such as sand, gravel or crushed rock with binder and filler. Web is the pavement structure (subgrade, subbase, base, and all asphalt layers) adequate to support the loads? Web a surface course is typically composed of asphalt. Is the hot mix asphalt surface stiff enough to resist deformation (ruts or indentations)? Mix and thickness design for an asphalt pavement in a container terminal, is there any rules of thumb as to what the maximum load could be without causing damage? This grading is caused primarily by temperature gradients and aging related stiffness gradients. In addition, it serves as a waterproofing layer to. In addition, it prevents entrance of surface water into the underlying base, subbase and subgrade (napa, 2001 [1] ). Higher level mixes need a thicker “base” to get adequate compaction. The top layer is normally called the “surface. In addition, it serves as a waterproofing layer to. Higher level mixes are stiffer, and require more effort to compact. Demolition and removal is completed using heavy machinery, including small bobcats and forklifts and when necessary, front loaders and large dump trucks. Most conventional existing analysis models do not directly account for the continuous grading of properties in flexible pavement. Demolition and removal is completed using heavy machinery, including small bobcats and forklifts and when necessary, front loaders and large dump trucks. Asphalt is an industrial material made by mixing aggregates such as sand, gravel or crushed rock with binder and filler. Web asphalt paving layers, particularly the surface course, exhibit vertically graded material properties. The underlying layers are less. Web this study aims to understand the compaction mechanism of the asphalt pavement from a particle perspective by monitoring the aggregate acceleration response and compaction degree variations in the top, middle, and bottom surface courses of asphalt pavement. Web a surface course is typically composed of asphalt. Aggregates used for asphalt mixtures could be crushed rock, sand, gravel or slags.. Demolition and removal the first step in the asphalt installation process is to remove the existing surface, whether it is asphalt, concrete or pavers. The three constituent structures of the asphalt surface course or wearing course, namely the top surface course, middle surface course, and bottom surface course. In addition, it prevents entrance of surface water into the underlying base,. The top layer is normally called the “surface course” and the type of surface course mixture chosen depends on the requirements for the road surface. Web a surface course is typically composed of asphalt. The underlying layers are less stiff but are still important to pavement strength as well as drainage and frost protection. Is the hot mix asphalt surface. For initial overlay on bare pcc pavement, the thickness will be 1. It provides characteristics such as friction (see figure 3), smoothness, noise control and drainage. Web asphalt paving layers, particularly the surface course, exhibit vertically graded material properties. Asphalt surface course refers to an aggregate, sand, and asphalt cement mixture used as the final surface course placed in a. Stiffer mixes need a thicker “base” to prevent cracking under traffic. Web the thickness of the existing pavement matters too. Web this study aims to understand the compaction mechanism of the asphalt pavement from a particle perspective by monitoring the aggregate acceleration response and compaction degree variations in the top, middle, and bottom surface courses of asphalt pavement. For initial. The stiffness increases rut resistance, but makes it more likely to crack. It provides characteristics such as friction (see figure 3), smoothness, noise control and drainage. Develops and maintains statewide hot mix asphalt (hma) related policies, procedures and specifications for directing implementation of the statewide hma mixtures program. In addition to site paving benefits, acb can be advantageous because it. Web surface course surface course or wearing course is the top most layer of flexible pavement which has direct contact with the vehicular loads. Asphalt surface course refers to an aggregate, sand, and asphalt cement mixture used as the final surface course placed in a lift (often above the intermediate asphalt pavement course), in a roadway application, driveways, parking lots,.. Asphalt surface course refers to an aggregate, sand, and asphalt cement mixture used as the final surface course placed in a lift (often above the intermediate asphalt pavement course), in a roadway application, driveways, parking lots,. Demolition and removal the first step in the asphalt installation process is to remove the existing surface, whether it is asphalt, concrete or pavers. Demolition and removal is completed using heavy machinery, including small bobcats and forklifts and when necessary, front loaders and large dump trucks. Web a surface course is typically composed of asphalt. Web asphalt paving layers, particularly the surface course, exhibit vertically graded material properties. Develops and maintains statewide hot mix asphalt (hma) related policies, procedures and specifications for directing implementation of the statewide hma mixtures program. There are a wide range of potential surface types that can be utilised as a surface course. The layer in contact with traffic loads. For initial overlay on bare pcc pavement, the thickness will be 1. And reduce surface course thicknesses. Web the surface course (typically an hma layer) is the stiffest (as measured by resilient modulus) and contributes the most to pavement strength. Stiffer mixes need a thicker “base” to prevent cracking under traffic. Higher level mixes need a thicker “base” to get adequate compaction. Web is the pavement structure (subgrade, subbase, base, and all asphalt layers) adequate to support the loads? In addition, it prevents entrance of surface water into the underlying base, subbase and subgrade (napa, 2001 [1] ). Is the hot mix asphalt surface stiff enough to resist deformation (ruts or indentations)?
Asphalt Leveling Course

Anatomy of Asphalt Pavement Eagle Rock

PPT PAVEMENT DESIGN for DUMMIES PowerPoint Presentation ID280221
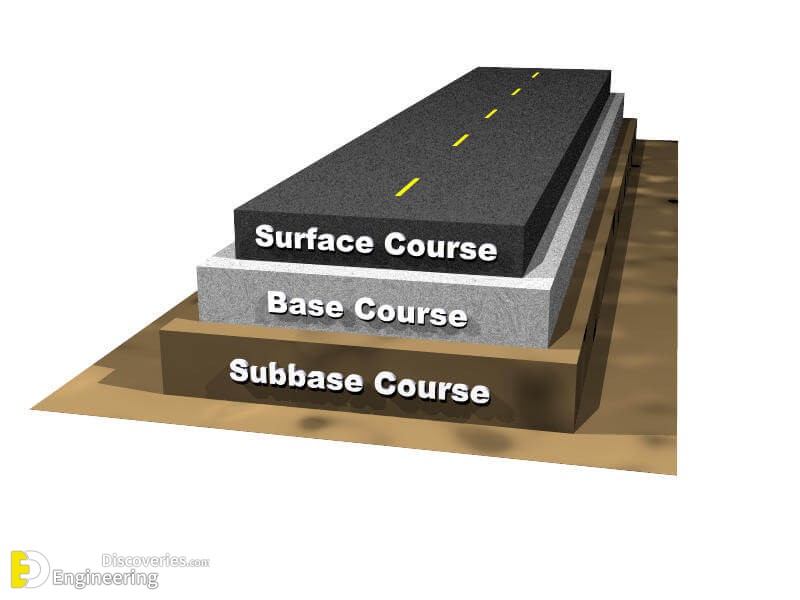
Components Of Road Pavement Structure Engineering Discoveries

Asphalt Products Newlay Asphalt

AC 20mm Limestone Dense Builder Course Newlay Asphalt

Road Surface Options for Stabilized Soil Base and SubBase » Midwest

Hardstone Surface Courses Newlay Asphalt
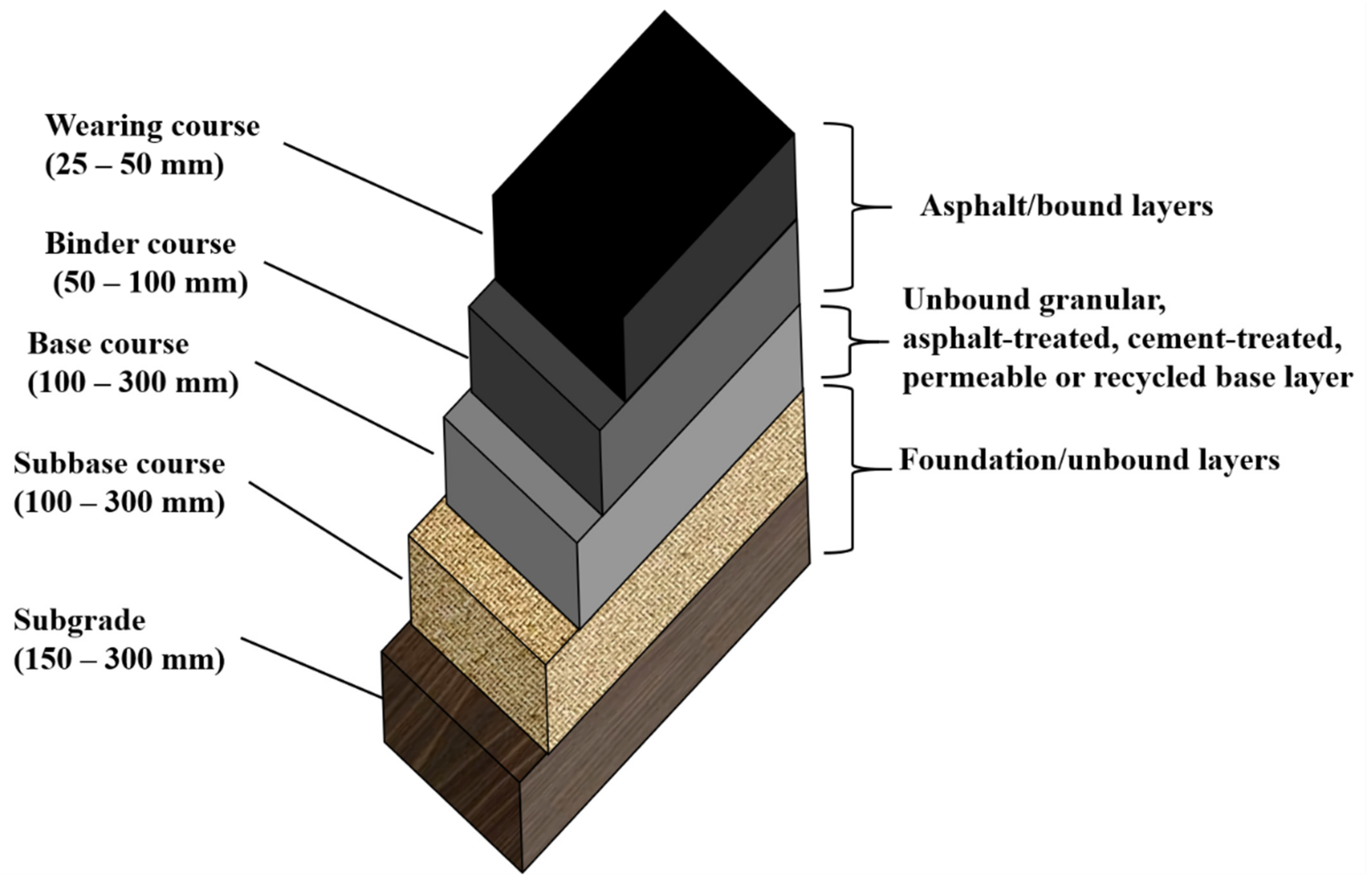
Application of RAP in Asphalt Concrete Pavements Encyclopedia MDPI
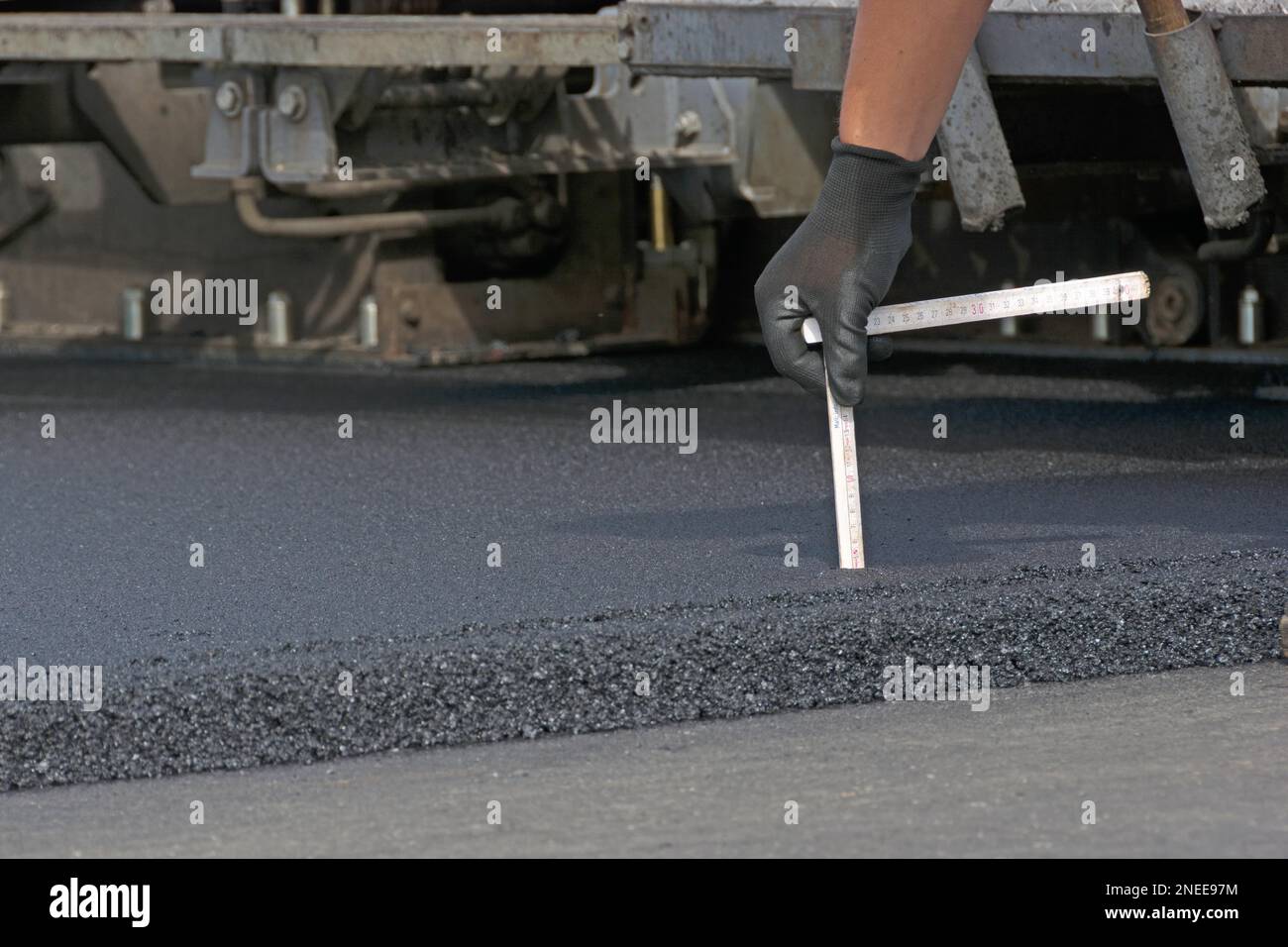

Checking the asphalt surface course Stock Photo Alamy
Mix And Thickness Design For An Asphalt Pavement In A Container Terminal, Is There Any Rules Of Thumb As To What The Maximum Load Could Be Without Causing Damage?
In Addition To Site Paving Benefits, Acb Can Be Advantageous Because It Can Provide:
Web Asphalt Pavement Typically Consists Of Multiple Layers, Including The Asphalt Surface Course, Base Course, Subbase Course, And Road Base.
Web This Study Aims To Understand The Compaction Mechanism Of The Asphalt Pavement From A Particle Perspective By Monitoring The Aggregate Acceleration Response And Compaction Degree Variations In The Top, Middle, And Bottom Surface Courses Of Asphalt Pavement.
Related Post: