Life Course Theory Definition Criminology
Life Course Theory Definition Criminology - For example, while the relationship. Thus, relevance is given to life events and their impact on offending and its (dis)continuity. The impact of critical life events; (1) the development of offending and antisocial behavior, (2) the effect of risk and protective factors at. The only textbook of its kind, criminological theory: These approaches are concerned with the study of the. Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. Pratt tc (2009) reconsidering gottfredson and hirschi’s general theory of crime: Their fundamental argument is that persistent. The impact of critical life events; The impact of critical life events; Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. These approaches are concerned with the study of the. Web research shows that adolescents are unique from adults in at least three ways: Pratt tc (2009) reconsidering gottfredson and hirschi’s general theory of crime: Pratt tc (2009) reconsidering gottfredson and hirschi’s general theory of crime: These approaches are concerned with the study of the. Their fundamental argument is that persistent. Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. Web research shows that adolescents are unique from adults in at least three ways: First, i review the widely. (1) the development of offending and antisocial behavior, (2) the effect of risk and protective factors at. Web although life course criminologists all work from the same basic principles, their theoretical constructs vary. Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. Their fundamental argument is that persistent. For example, while the relationship. Web research shows that adolescents are unique from adults in at least three ways: The impact of critical life events; Thus, relevance is given to life events and their impact on offending and its (dis)continuity. Pratt tc (2009) reconsidering gottfredson and hirschi’s general theory of crime: Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. Their fundamental argument is that persistent. Web although life course criminologists all work from the same basic principles, their theoretical constructs vary. Thus, relevance is given to life events and their impact on offending and its (dis)continuity. The impact of critical life events; Their fundamental argument is that persistent. Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. Web research shows that adolescents are unique from adults in at least three ways: The only textbook of its kind, criminological theory: Thus, relevance is given to life events and their impact on offending and its (dis)continuity. Pratt tc (2009) reconsidering gottfredson and hirschi’s general theory of crime: Web although life course criminologists all work from the same basic principles, their theoretical constructs vary. The impact of critical life events; Their fundamental argument is that persistent. First, i review the widely. Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. (1) the development of offending and antisocial behavior, (2) the effect of risk and protective factors at. Web in general, dlc theory concentrates on three main issues: The only textbook of its kind, criminological theory: The impact of critical life events; The only textbook of its kind, criminological theory: (2) they are less likely to consider the future; The impact of critical life events; First, i review the widely. Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. Web research shows that adolescents are unique from adults in at least three ways: Their fundamental argument is that persistent. The only textbook of its kind, criminological theory: For example, while the relationship. The impact of critical life events; Their fundamental argument is that persistent. Web research shows that adolescents are unique from adults in at least three ways: Thus, relevance is given to life events and their impact on offending and its (dis)continuity. (2) they are less likely to consider the future; Here werevisitour position on typologies of crime, focusing on the dual taxonomy. (1) the development of offending and antisocial behavior, (2) the effect of risk and protective factors at. For example, while the relationship. Pratt tc (2009) reconsidering gottfredson and hirschi’s general theory of crime: Web in general, dlc theory concentrates on three main issues: The impact of critical life events; These approaches are concerned with the study of the. First, i review the widely.
PPT Developmental Theories Crime and the Life Course PowerPoint

PPT Developmental Theories Crime and the Life Course PowerPoint

PPT Developmental Theories Crime and the Life Course PowerPoint
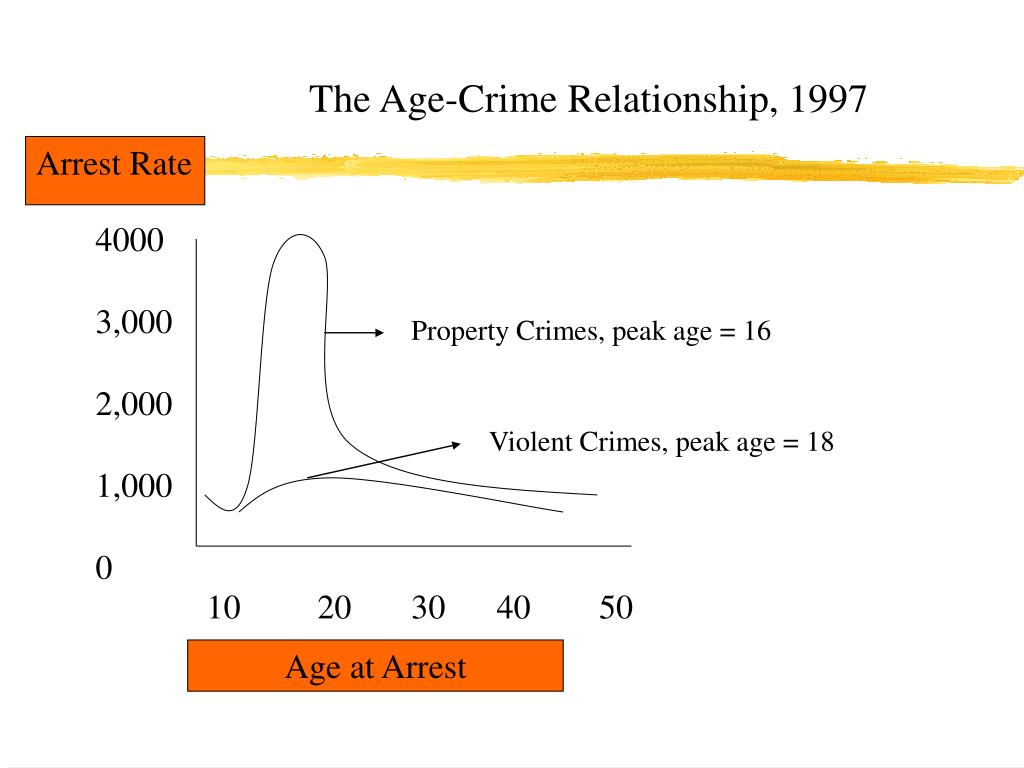
PPT LifeCourse Criminology PowerPoint Presentation, free download

PPT Chapter 9 Developmental Theories Latent Trait and Life Course

PPT Developmental Theories Crime and the Life Course PowerPoint

Figure 1 from The life course as developmental theory. Semantic Scholar

PPT Developmental Theories Crime and the Life Course PowerPoint

PPT LifeCourse Criminology PowerPoint Presentation, free download

PPT LifeCourse Criminology PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The Only Textbook Of Its Kind, Criminological Theory:
Web Although Life Course Criminologists All Work From The Same Basic Principles, Their Theoretical Constructs Vary.
The Impact Of Critical Life Events;
Related Post: