Life Course Theory Sampson And Laub
Life Course Theory Sampson And Laub - The organizing principle of sampson and laub's theory is social control, i.e., that delinquency is more likely when an individual's bond to society is weak or broken. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; A life course theory of cumulative disadvantage and the stability of delinquency. Sampson harvard university john h. Web last updated on 12/04/2012 neighborhoods project crime and the life course the social science of cities environmental inequality sampson, robert j, and john h laub. In developmental theories of crime and delinquency, ed. Web sampson, robert j., and john h. (advances in criminological theory, volume 7), edited by terence p. Thornberry (ed.), developmental theories of crime and delinquency (pp. Laub’s age graded theory or theory of turning points describe the change in the crime load of individuals as a function of biographical events. Sampson harvard university john h. We first contextualize the theory by discussing its origins. Laub’s age graded theory or theory of turning points describe the change in the crime load of individuals as a function of biographical events. Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: Web one of the most well established assertions in criminology is that of the relationship between crime and age (e.g. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; By concentrating on the teenage years, sociological perspectives on crime have Laub’s age graded theory or theory of turning points. We first contextualize the theory by discussing its origins. Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: Sampson gary sweeten arizona state university abstract the abstract. In the 1940s, sheldon and eleanor gluck conducted a longitudinal study of troubled boys in boston. In developmental theories of crime and delinquency, ed. In developmental theories of crime and delinquency, ed. In the 1940s, sheldon and eleanor gluck conducted a longitudinal study of troubled boys in boston. Web sampson, robert j., and john h. Although criminal behavior does peak in the teenage years, evidence reviewed below indicates an early onset of delinquency as well as continuity of criminal behavior over the life course.. In developmental theories of crime and delinquency, ed. Web [also known as: Disruption of relations between individuals and institutions that provide social capital; Sampson & laub, 1992, 1998; They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating data ever studied by criminologists. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: Disruption of relations between individuals and institutions that provide social capital; The organizing principle of sampson and laub's theory is social control, i.e., that delinquency is more likely when an individual's bond to society is weak or broken. (advances in. And the influence of structural disadvantage. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating data ever studied by criminologists. Laub university of maryland, college park r.j. Although criminal behavior does peak in the teenage years, evidence reviewed below indicates an early onset of delinquency as well as continuity of criminal behavior over the life course. Web [also known as: Laub’s age graded theory or theory of turning points describe the change in the crime load of individuals as a function of biographical events. Mcara & mcvie,. Sampson & laub, 1992, 1998; Web one of the most well established assertions in criminology is that of the relationship between crime and age (e.g. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; Although criminal behavior does peak in the teenage years, evidence reviewed below indicates an early onset of delinquency as well as continuity of criminal behavior over the. Laub university of maryland, college park r.j. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; The organizing principle of sampson and laub's theory is social control, i.e., that delinquency is more likely when an individual's bond to society is weak or broken. Although criminal behavior does peak in the teenage years, evidence reviewed below indicates an early onset of delinquency. Sampson & laub, 1992, 1998; They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating data ever studied by criminologists. In developmental theories of crime and delinquency, ed. Although criminal behavior does peak in the teenage years, evidence reviewed below indicates an early onset of delinquency as well as continuity of criminal behavior over the life course. [they] acknowledge the importance of childhood behaviors and individual differences, but reject the implication that social factors have little relevance. Sampson gary sweeten arizona state university abstract the abstract. Sampson harvard university john h. Web a test of sampson and laub's (1990, 1993) life course theory is conducted to examine whether racial/ethnic differences in frequency of drunkenness associated with age remain once adult socialbond measures are held constant. By concentrating on the teenage years, sociological perspectives on crime have Mcara & mcvie, 2012), in which developmentally orientated researchers attempt to explain. Web on the basis of their findings, sampson and laub developed a theory of informal social control over the life course. In the 1940s, sheldon and eleanor gluck conducted a longitudinal study of troubled boys in boston. Laub university of maryland, college park r.j. A life course theory of cumulative disadvantage and the stability of delinquency. Web [also known as: Web sampson, robert j., and john h.
PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Moffitt’s
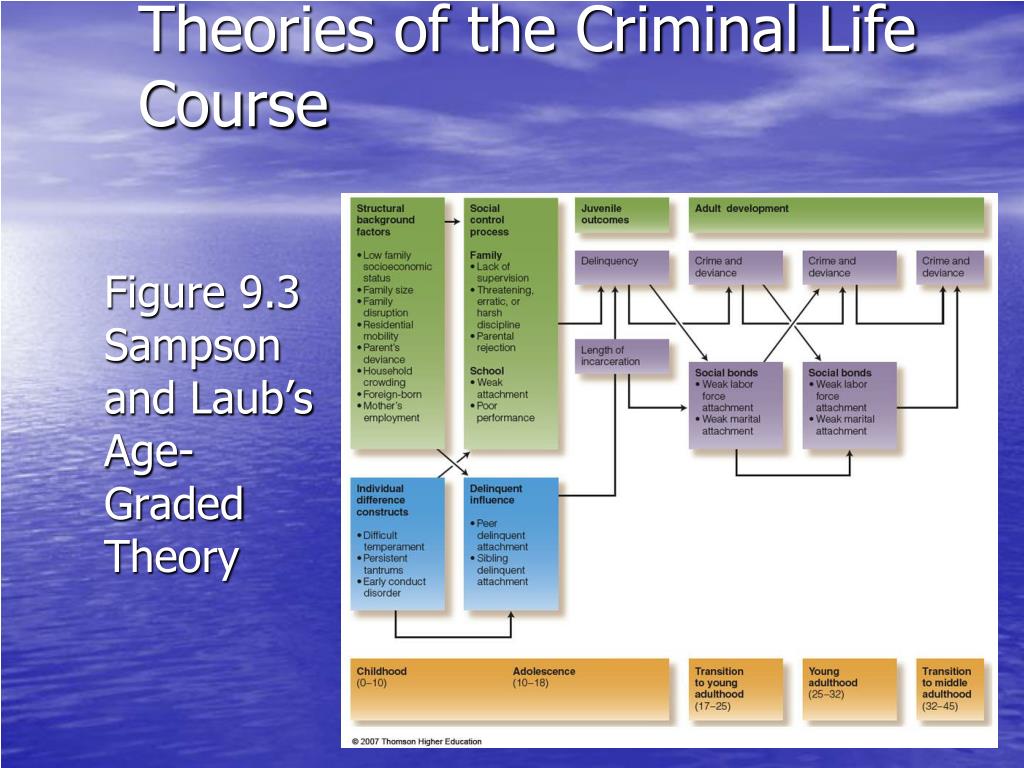
PPT Chapter 9 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1292754

PPT Chapter 9 Developmental Theories Latent Trait and Life Course
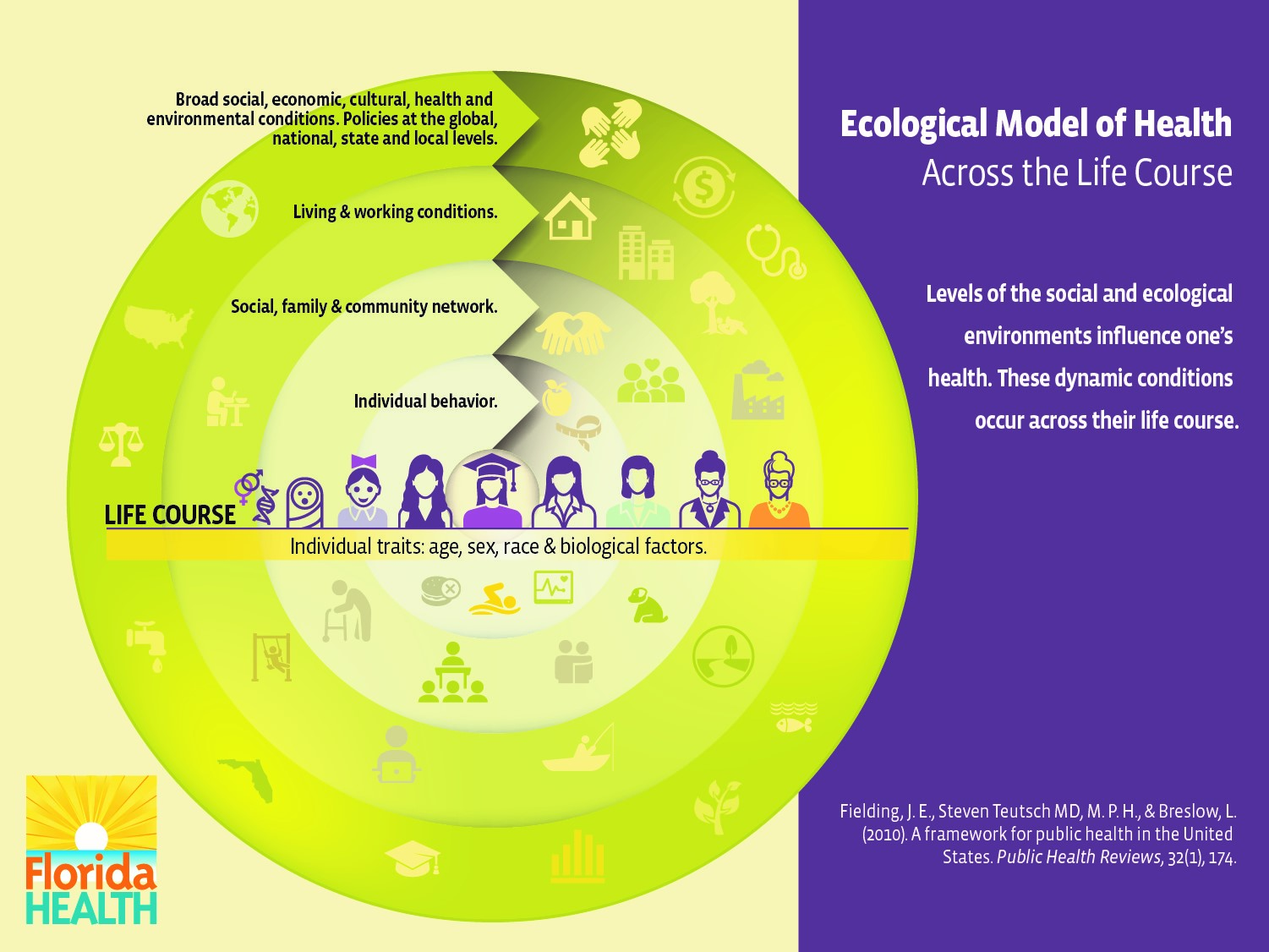
The Life Course Theory Florida Department of Health

Age Graded Theory/ Turning Points (Sampson and Laub) SozTheo

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Moffitt’s

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Terrie

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Terrie

Life course theory Tahap perkembangan, Manusia, Teori

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Terrie
(Advances In Criminological Theory, Volume 7), Edited By Terence P.
The Organizing Principle Of Sampson And Laub's Theory Is Social Control, I.e., That Delinquency Is More Likely When An Individual's Bond To Society Is Weak Or Broken.
Trajectories Of Crime Among Delinquent Boys Followed To Age 70* Robert J.
Web One Of The Most Well Established Assertions In Criminology Is That Of The Relationship Between Crime And Age (E.g.
Related Post: