Magnetic Course
Magnetic Course - Web course, track, route and heading. That's because map projections tend to distort measurements at different points. Magnetic north is currently over northern canada. Web you’ll apply a further connection to true course and heading to give you a magnetic course to steer during the planning stage. This will be what you use in your navigational flight plan. Magnetic heading is your your true course modified by winds and variation. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. It might be the same as your magnetic heading in perfect conditions, with no winds. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in the middle of the flight leg. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. Web true course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. First, we must work out everything in degrees true before adding or subtracting magnetic variation.. Ground track is the course that the aircraft is. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. Web course, track, route and heading. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in the middle of the. First, we must work out everything in degrees true before adding or subtracting magnetic variation. Ground track is the course that the aircraft is. Web course, track, route and heading. The angular difference between true and magnetic north is called magnetic variation. This will be what you use in your navigational flight plan. That's because map projections tend to distort measurements at different points. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole. Ground track is the course that the aircraft is. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in the middle of the flight leg. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. Web course, track, route and heading. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in the middle of the flight leg. Web you’ll apply a further connection to true course and heading to give you a magnetic course to steer during the planning stage. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole. Magnetic heading is your your. Web magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. You'll get the most accurate tc if you measure it in the middle of the flight leg. Ground track is the course that the aircraft is. The difference is due to. It might be the same as your magnetic heading in perfect conditions, with no winds. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. Web course, track, route and heading. This will be what you use in your navigational flight plan. That's because map projections tend to distort. It might be the same as your magnetic heading in perfect conditions, with no winds. Magnetic north is currently over northern canada. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. First, we must work out everything in degrees true before adding or subtracting magnetic variation. The difference. Magnetic heading is your your true course modified by winds and variation. That's because map projections tend to distort measurements at different points. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. First, we must work out everything in degrees true before adding or subtracting magnetic variation. The. Ground track is the course that the aircraft is. Web true course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. Magnetic heading is your your true course modified by winds and variation. Magnetic north is currently over northern canada. Web course, track, route and heading. Web true course (tc) is the direction or heading you calculate when plotting your flight's route on a sectional chart using a navigation plotter. Web a pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a 'track' or 'course' to fly in degrees true. Web you’ll apply a further connection to true course and heading to give you a magnetic course to steer during the planning stage. First, we must work out everything in degrees true before adding or subtracting magnetic variation. Web course, track, route and heading. Magnetic north is currently over northern canada. The angular difference between true and magnetic north is called magnetic variation. Ground track is the course that the aircraft is. Magnetic heading is your your true course modified by winds and variation. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. Web magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass.
Playtable Course Theraplay

True and Course Courses and Headings in Navigation (Part 1/2
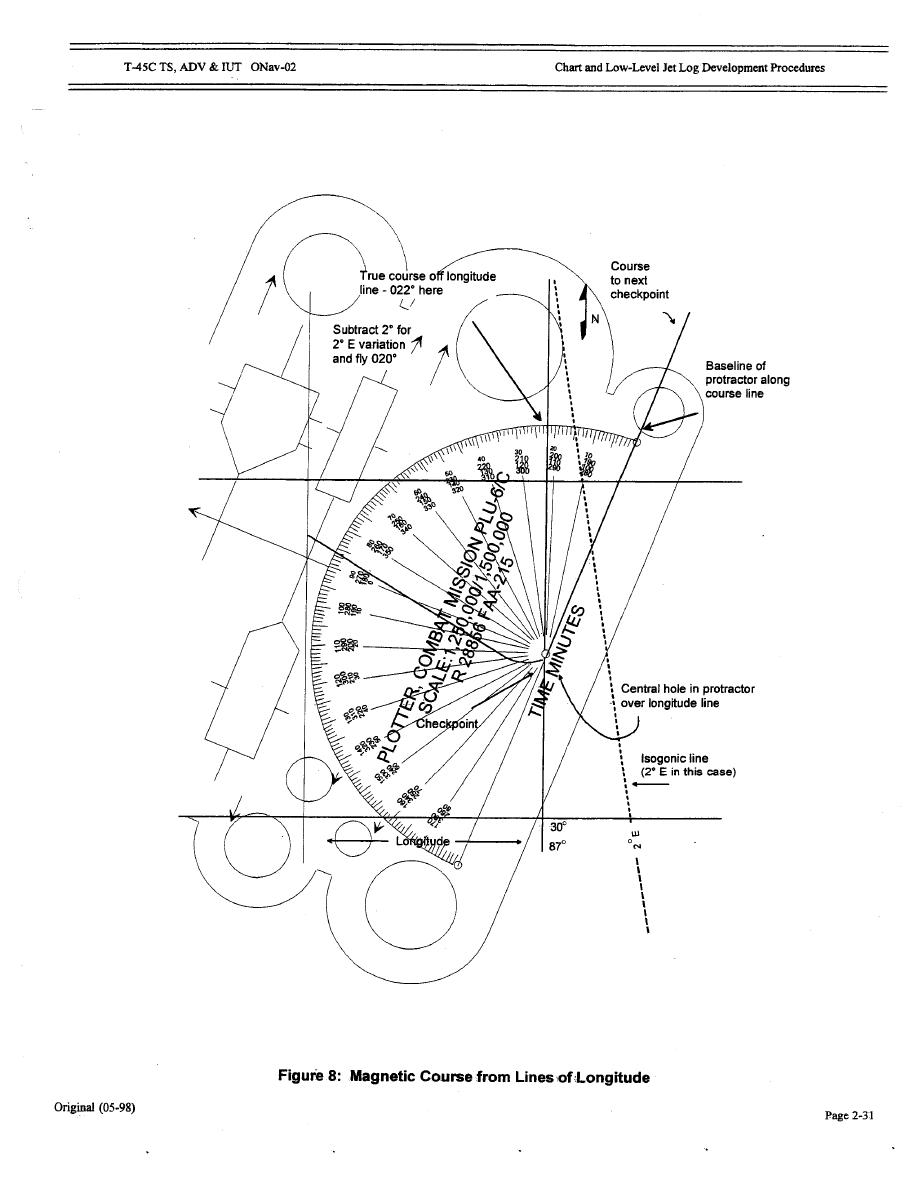
Figure 8. Course from Lines of Longitude
field
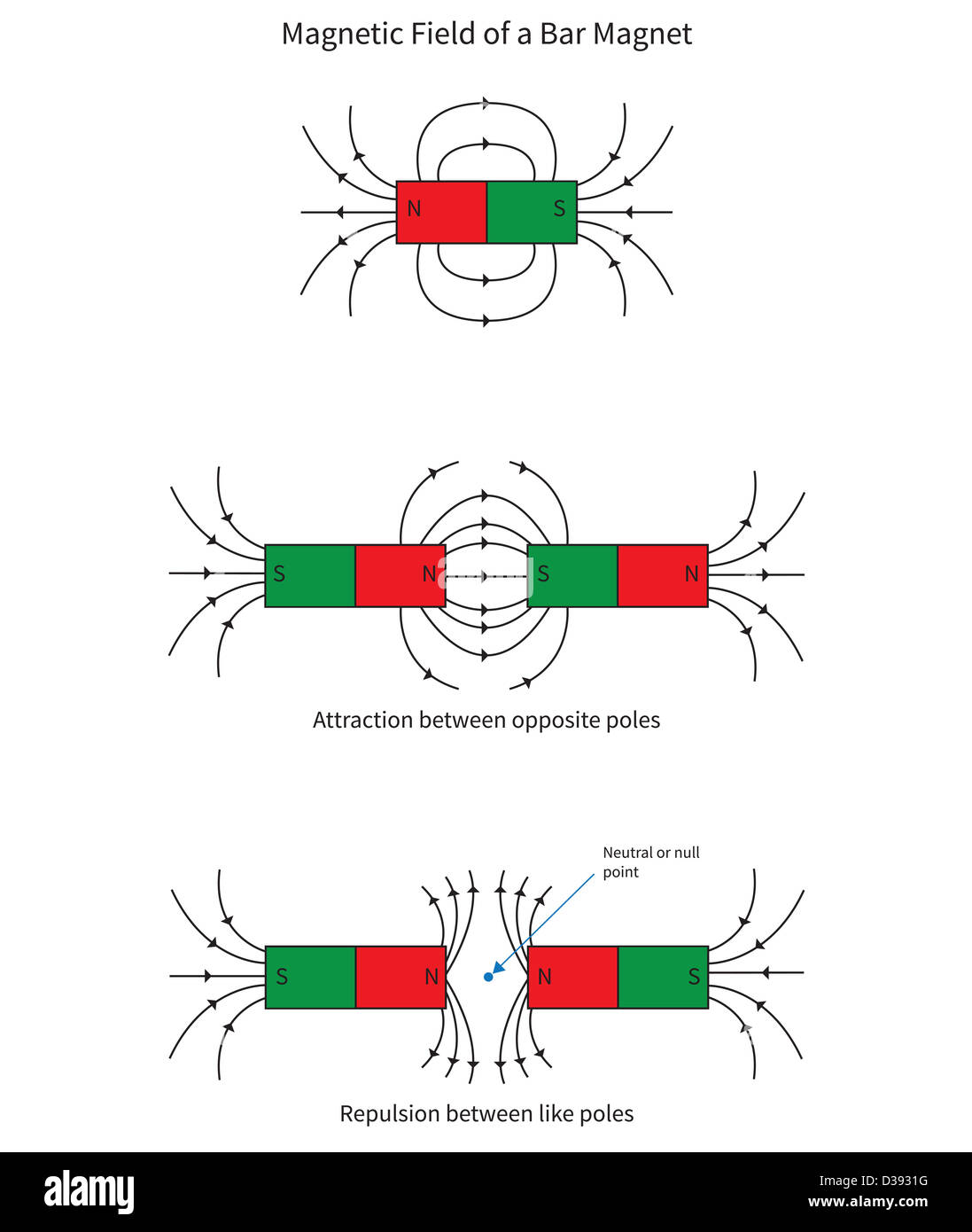
Fields Two

Earth's field Stock Vector Images Alamy
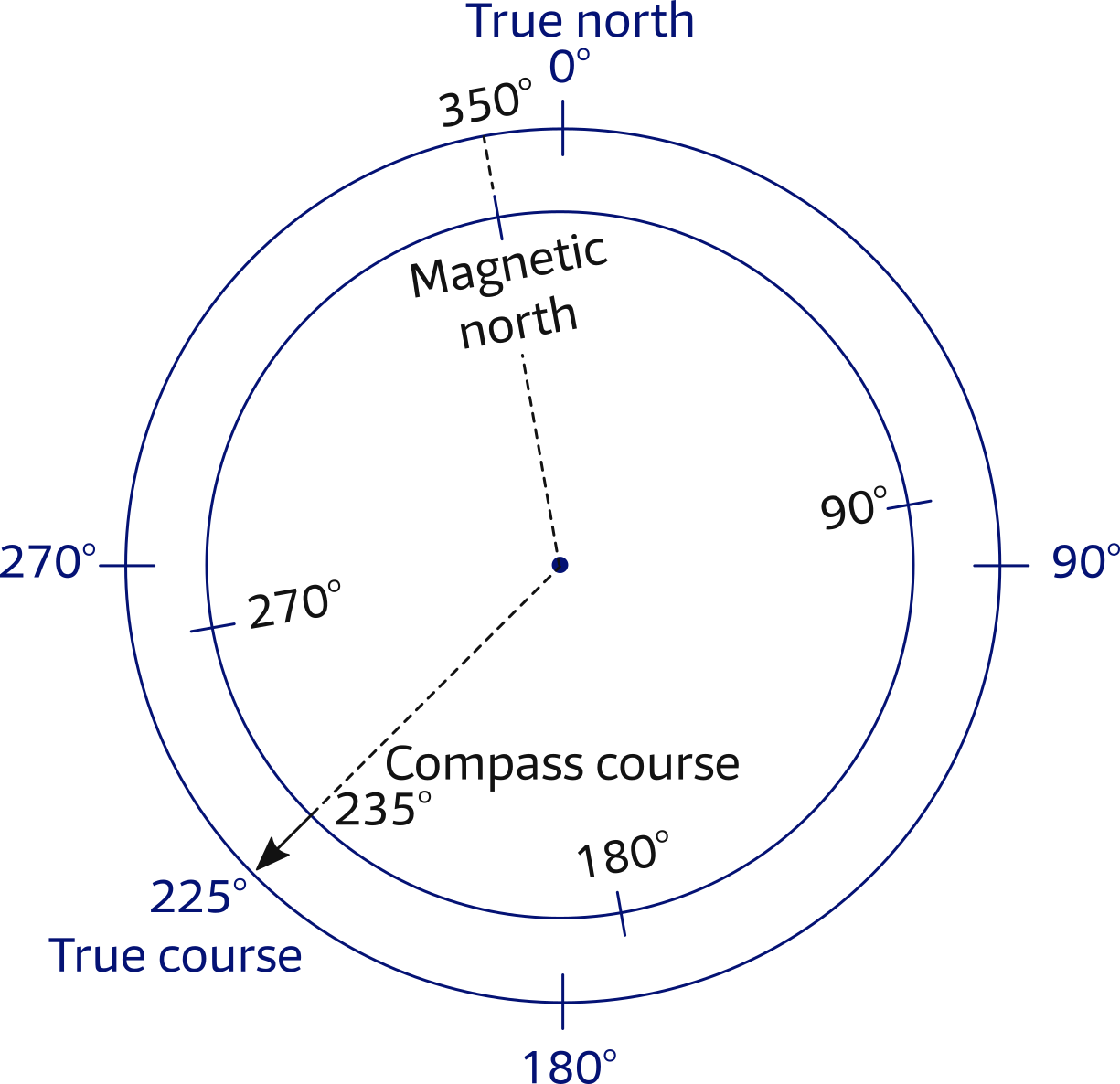
Marine navigation courses compass ASA RYA

(Chapter 24 BUNDLE) A level Physics Fields fields

Understanding Course YouTube

Playtable Course Theraplay
You'll Get The Most Accurate Tc If You Measure It In The Middle Of The Flight Leg.
This Will Be What You Use In Your Navigational Flight Plan.
That's Because Map Projections Tend To Distort Measurements At Different Points.
It Might Be The Same As Your Magnetic Heading In Perfect Conditions, With No Winds.
Related Post: