Sampson And Laub Life Course Theory
Sampson And Laub Life Course Theory - Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating. [they] acknowledge the importance of childhood behaviors. We first contextualize the theory by. Web neighborhoods project crime and the life course the social science of cities environmental inequality sampson, robert j, and john h laub. Sampson, robert j., and john h. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; Web [also known as: Web sampson and laub (2005) argue that child risk factors have very limited predictive power across the life course. Risk is not destiny (developmental crime. Web [also known as: A life course theory of cumulative disadvantage and the stability of delinquency. We first contextualize the theory by. Thornberry (ed.), developmental theories of crime. Risk is not destiny (developmental crime. A life course theory of cumulative disadvantage and the stability of delinquency. Web on the basis of their findings, sampson and laub developed a theory of informal social control over the life course. It outlines both the 1993 and 2003 versions of the. Sampson, robert j., and john h. In this article we contest the idea that individual. In this article we contest the idea that individual. Sampson, robert j., and john h. Web sampson and laub (2005) argue that child risk factors have very limited predictive power across the life course. [they] acknowledge the importance of childhood behaviors. It outlines both the 1993 and 2003 versions of the. Web neighborhoods project crime and the life course the social science of cities environmental inequality sampson, robert j, and john h laub. Risk is not destiny (developmental crime. It outlines both the 1993 and 2003 versions of the. We first contextualize the theory by. Disruption of relations between individuals and. We first contextualize the theory by. In this article we contest the idea that individual. A life course theory of cumulative disadvantage and the stability of delinquency. Risk is not destiny (developmental crime. [they] acknowledge the importance of childhood behaviors. Web [also known as: In this article we contest the idea that individual. Sampson, robert j., and john h. Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: Disruption of relations between individuals and. Web [also known as: Sampson, robert j., and john h. In this article we contest the idea that individual. Web neighborhoods project crime and the life course the social science of cities environmental inequality sampson, robert j, and john h laub. We first contextualize the theory by. They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating. Web neighborhoods project crime and the life course the social science of cities environmental inequality sampson, robert j, and john h laub. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; Web on the basis of their findings, sampson and laub developed a theory of informal social control over the life. Thornberry (ed.), developmental theories of crime. Web on the basis of their findings, sampson and laub developed a theory of informal social control over the life course. They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating. Web neighborhoods project crime and the life course the social science of cities environmental inequality sampson, robert j, and john h laub. In. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; We first contextualize the theory by. A life course theory of cumulative disadvantage and the stability of delinquency. Sampson, robert j., and john h. Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: They developed this theory using some of the most fascinating. Sampson, robert j., and john h. It outlines both the 1993 and 2003 versions of the. Web on the basis of their findings, sampson and laub developed a theory of informal social control over the life course. Web [also known as: Web abstract sampson and laub argue that crime causes have three sources: Disruption of relations between individuals and. Thornberry (ed.), developmental theories of crime. We first contextualize the theory by. Weak social bonds to family, school, and work; [they] acknowledge the importance of childhood behaviors. Risk is not destiny (developmental crime.
Age Graded Theory/ Turning Points (Sampson and Laub) SozTheo

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Moffitt’s

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Terrie

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Moffitt’s

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Terrie
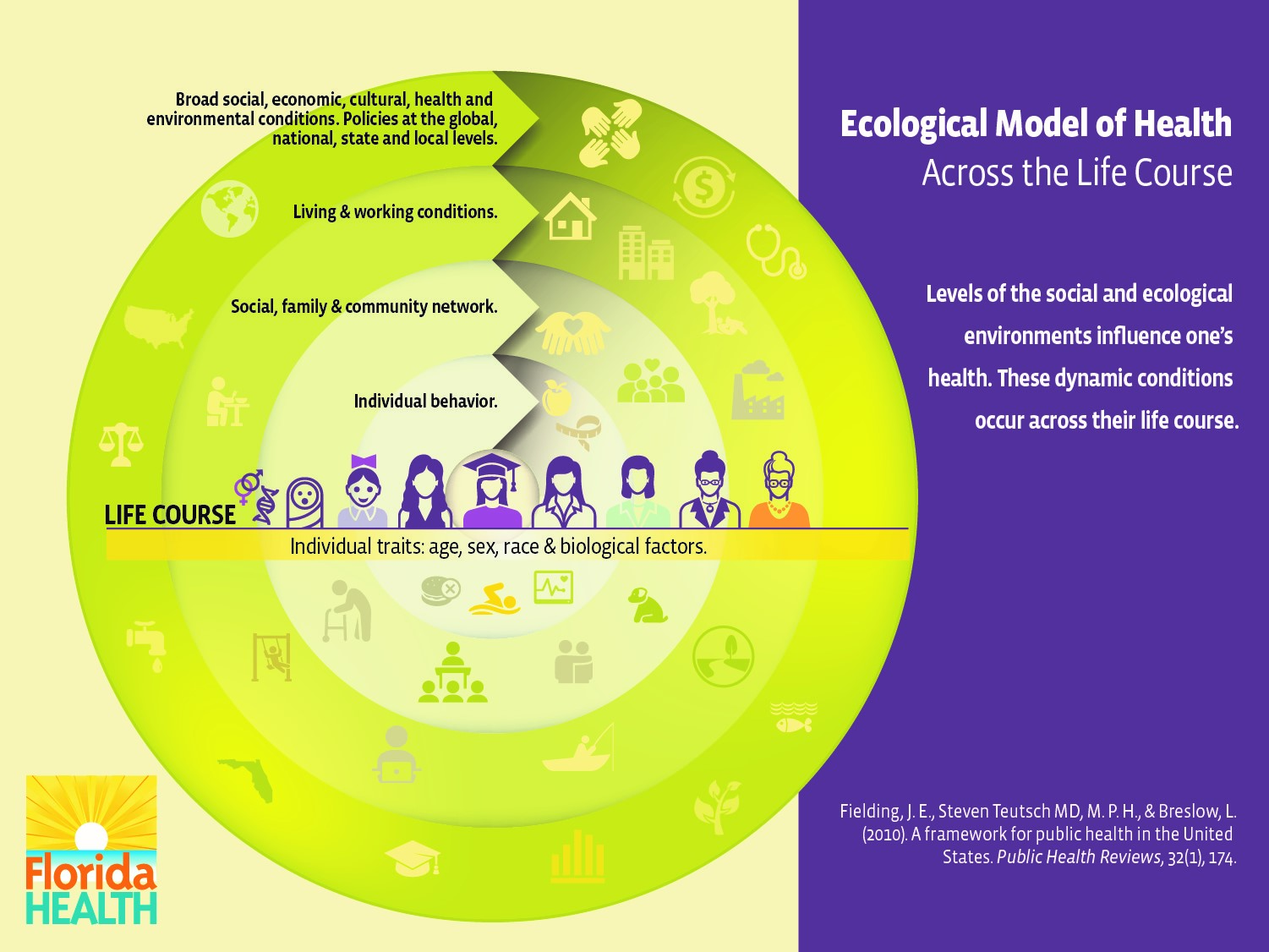
The Life Course Theory Florida Department of Health

PPT Chapter 9 Developmental Theories Latent Trait and Life Course

Developmental Psychologists Study the ________ That Occur Throughout

PPT Chapter 9 Developmental Theories Latent Trait and Life Course

PPT Review Lifecourse Framework Review Sampson and Laub Terrie
A Life Course Theory Of Cumulative Disadvantage And The Stability Of Delinquency.
Web Neighborhoods Project Crime And The Life Course The Social Science Of Cities Environmental Inequality Sampson, Robert J, And John H Laub.
In This Article We Contest The Idea That Individual.
Web Sampson And Laub (2005) Argue That Child Risk Factors Have Very Limited Predictive Power Across The Life Course.
Related Post: